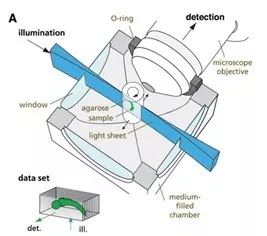
Fast and reliable in situ imaging of biological samples to reveal dynamic processes associated with complex multicellular organisms has always been a major goal of optical imaging. Although traditional laser confocal microscopy has excellent 3D fluorescence imaging capabilities and provides very high spatial resolution, in some experiments, imaging speed is not fast enough and photobleaching problems cannot be ignored. The proposed light film technology solves these problems well while maintaining excellent spatial resolution. The Leica DLS Light Film Imaging Module can be built directly onto a confocal microscope to upgrade new skills for confocal systems: fast 3D imaging, lower phototoxicity, light operation and fast 3D imaging in vivo. Common applications for Leica light microscopy systems: 1. Fast 3D imaging Left: seaweed 3D reconstruction + puzzle, autofluorescence Right: Drosophila eye 3D reconstruction 2. Fast and long-term 3D imaging of the living body, capturing the entire dynamic process Zebrafish heart beat 3D reconstruction 3. The only system that can combine confocal and light film to achieve follow-up of optical operation Tracking the growth process of the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica [1] Tracking the growth of fungi and the formation of biofilms is of great importance in the food and pharmaceutical industries: understanding the patterns and mechanisms of fungal growth can help us use beneficial fungi more effectively and contain harmful bacteria. The growth of fungi at different developmental stages depends on intracellular activity and the biochemical environment in which it is located. However, confocal microscopy and electron microscopy techniques that are currently used are not perfect for this task. Published in ChemPhysChem's "Exploring Morphological and Biochemical Linkages in Fungal Growth with Label-Free Light Sheet Microscopy and Raman Spectroscopy" using Leica light sheet technology DLS, directly using the autofluorescence of the fungus itself: due to different metabolic states, this autofluorescence "specificity The mark "is on the spores, while the hyphae are essentially absent. It can be seen from the figure that the distribution of spores is clearly seen by using DLS: toward the top, a gradient distribution, and the closer to the top, the greater the density of spores. The imaging depth is 1.1mm, which fully satisfies the study of intact fungi. This gradient distribution indicates that there is an internal growth regulation mechanism in the fungus. Combined with Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS), the complex physicochemical interactions are directly related to the morphological characteristics of fungal growth, providing a study of the relationship between secondary metabolites and fungal growth. Very good tool. Let's first take a look at what is the light microscopy technology [2]: Fluorescent samples are excited from the side of the sample using a beam of light, detected using CCD or sCMOS, and the illumination path and the fluorescence detection path are perpendicular to each other. Since the plane in which the sample is excited is the imaging plane, there is no defocus excitation, and optical slicing can be automatically obtained, thereby minimizing photobleaching and optical damage. The light film microscopy system uses CCD or sCMOS imaging, and the speed is usually tens of frames per second or even hundreds of frames. Therefore, by moving the sample under the light sheet to inject the incident light beam into different planes, the whole can be easily and very quickly obtained. 3D map of the organization. Then we will also find that traditional light microscopy microscopes usually require the installation of dedicated optics in a separate system, where the illumination and detection objectives are arranged perpendicular to each other. However, in practical applications, many times we need both light and confocal functions. The Leica TCS SP8 DLS creatively combines optical and confocal imaging : the light is placed directly on the confocal platform, and the unique TwinFlect mirror unit allows the excitation beam to be incident on the sample from both left and right, with uniform illumination. and eliminate the natural double-sided lighting dark areas to ensure that the interference levels of resolution cells. The fast imaging speed , high resolution and low phototoxicity allow the sample to retain its biological activity in the system, completing long-lived biological culture and imaging for hours or even days. Light sheet microscope has never been easy, but at the same time without sacrificing the confocal functionality, the joint can also be achieved using a focused light sheet microscope and common, complete activation light, the light conversion operation and follow-up experiments. references [1] Siddhanta, S., et al. (2017). "Exploring Morphological and Biochemical Linkages in Fungal Growth with Label-Free Light Sheet Microscopy and Raman Spectroscopy." Chemphyschem 18(1): 72-78. [2] Huisken, J., et al. (2004). "Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by selective plane illumination microscopy." Science 305 (5686): 1007-1009.
There are two kinds of external fixations for pelvic fractures, namely temporary fixation and therapeutic fixation.
Temporary fixation depends on on-site assistance. Assuming that the patient has serious open injury, severe hemorrhagic shock, and serious fracture dislocation, the rescue personnel will provide temporary external fixation support to maintain the stability of the pelvis, reduce secondary injuries, and correct the continuous aggravation of hemorrhagic loss on the scene. The therapeutic external fixation stent is used to correct the dislocation of the fracture through routine examination after admission, evaluation of the injury, and external fixation installation through treatment, maintain the relative stability of the fracture, create a very quiet environment for the fracture healing, and lay the foundation for the healing of the fracture. External fixation is an important method for pelvic fractures.
Pelvic External Fixation,pelvic ex fix,Pelvic External Fixator,pelvic fixator Jiangsu Aomed Ortho Medical Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.aomedortho.com
· Real-time imaging of three-dimensional cell culture, tissue culture, and organ culture.
· Combine confocal or two-photon laser microscopy to complete optical stimulation and tracking, and the observation and experimental methods are more flexible. 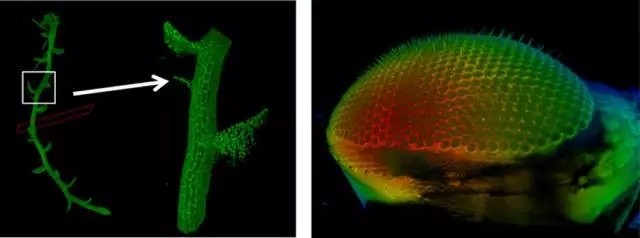
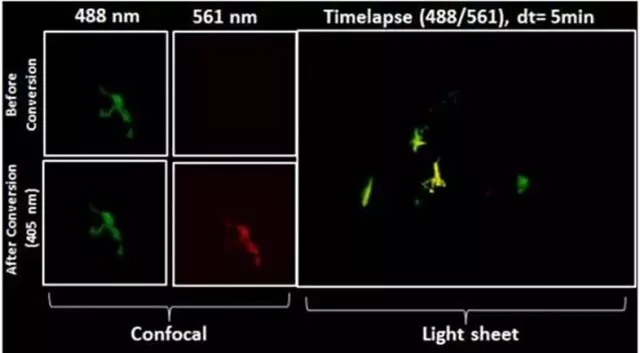
After zebrafish neuron conversion (Kaede), the movement of the cell is continuously recorded, and the video is as follows 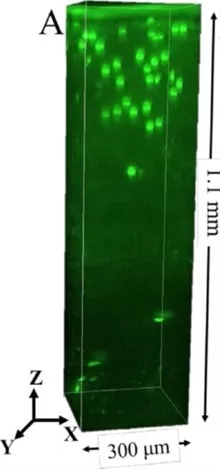
Leica light film imaging principle